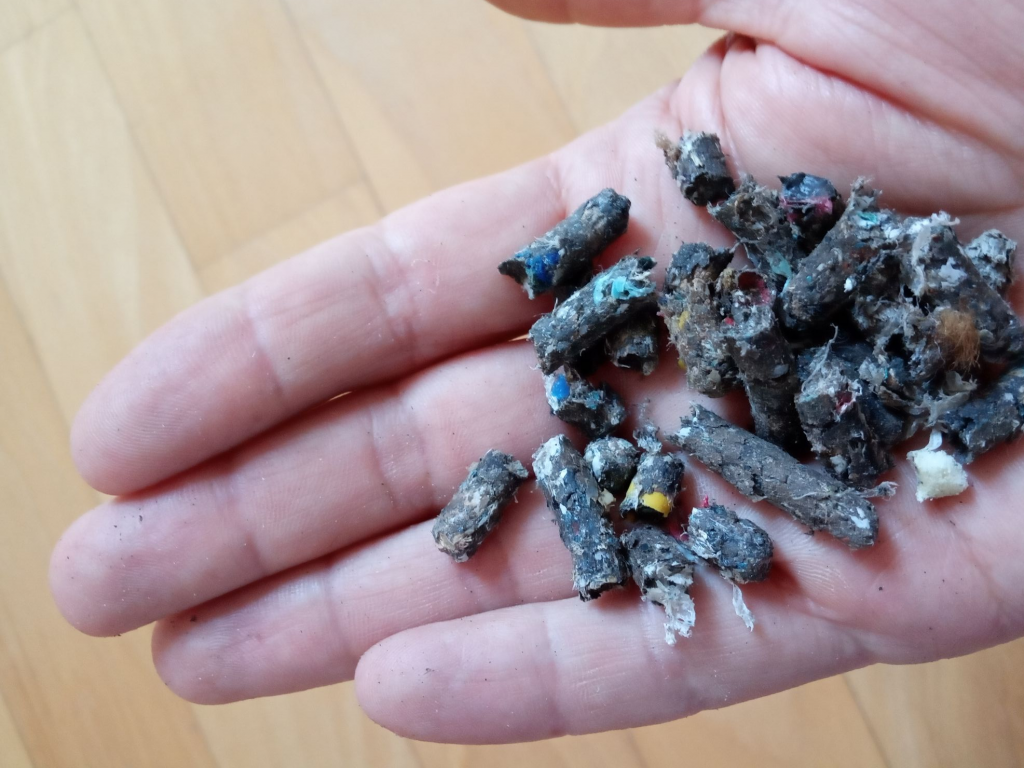
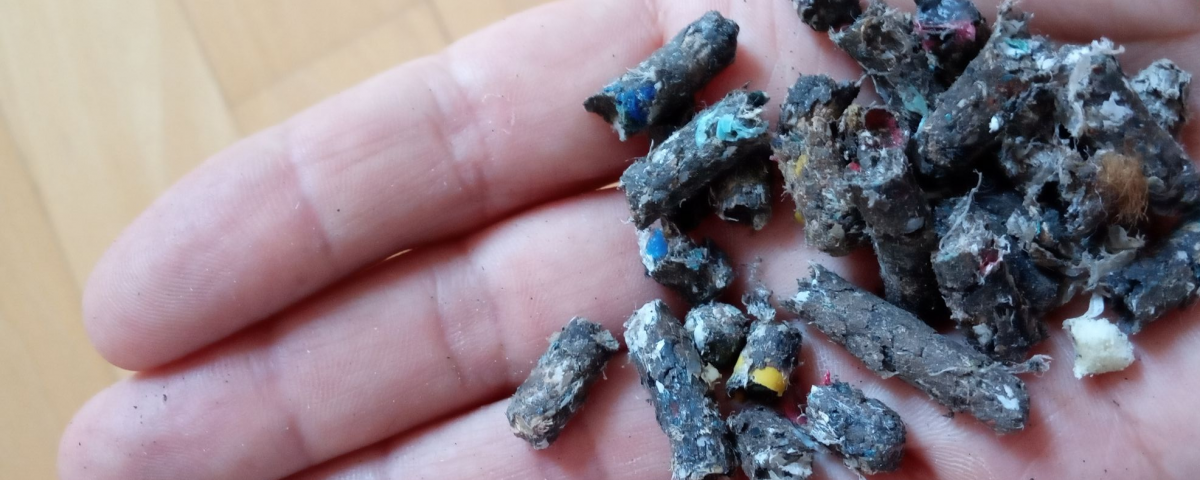
RDF
Waste to Energy in Europe
03/12/2017
Germany imported over 1.7 million tonnes of RDF in 2015
08/11/2018RDF means ‘Refuse Derived Fuel’. This is an alternative fuel. This is a secondary material made from sorting of waste. Its composition is a mix of paper, plastic, textile, rubber, wood. RDF production from MSW is most active in European Member States with high levels of MSW (Municipal Solid Waste) source separation and recycling (i.e. Austria, Germany, Netherlands are the best examples), as the recycling activity generates non-recyclable high calorific residues suitable as RDF. The total quantities of RDF produced from MSW in the European Union have been estimated to amount to about 3 million tons. The capacity for RDF production from MSW and Industrial not hazardous Waste is on the increase in Austria, Belgium, Finland, Italy and Netherlands with new MBT (Mechanical Biological Treatment) plants being built. Use of RDF in coal power plants and cement works, due to the effective substitution of primary fossil fuels, shows a large number of ecological advantages when they are compared with the alternative combustion in a MSWI as long as the plants comply with the New Waste Incineration Directive 2000/76. The most important regulation is the Waste Incineration Directive (2000/76/EC). It introduces emissions limits for co-incineration of waste for energy recovery. Legislation regarding waste management also influence RDF production and utilization as it requires Member States to move waste away from landfill and into options which are higher in the waste management hierarchy such as incineration and/or recycling. 1) RDF – abbreviation of refuse derived fuel – is a fuel that is produced from a combination of non-recyclable commercial and industrial waste. This fuel contains different types of plastics, textile, rubber, wood and paper. Recyclables, such as glass and metal, are taken by waste sorters. The remaining material is useful to either be processed further into a higher quality alternative fuel, or can be used in waste to energy facilities. Waste incinerators combust RDF as fuel to generate heat and electricity. This is called energy recovery. This application prevents waste from ending up in landfill. Other RDF users are fuel producers. They use RDF with a high calorific value. The material is very suited to get processed into SRF, which is typically done via a mechanical process. After processing the material is suited to be used as an alternative for fossil fuels such as bituminous coal.
SRF two-dimensional 50 x 50 mm
2) SRF – abbreviation of solid recovered fuel – is RDF upgraded to a fuel that consists of smaller fractions and more energy content. Processing RDF further upgrades the waste material, first more recyclables are taking out and then the non-recyclable residue is being used as fuel which is mostly suited to replace primary fossil fuels. Depending on the quality and application, SRF can substitute at least 70% of the primary fuels, used in a kiln or boiler.
Reverse Technology allows the mechanical separation of mixed industrial waste
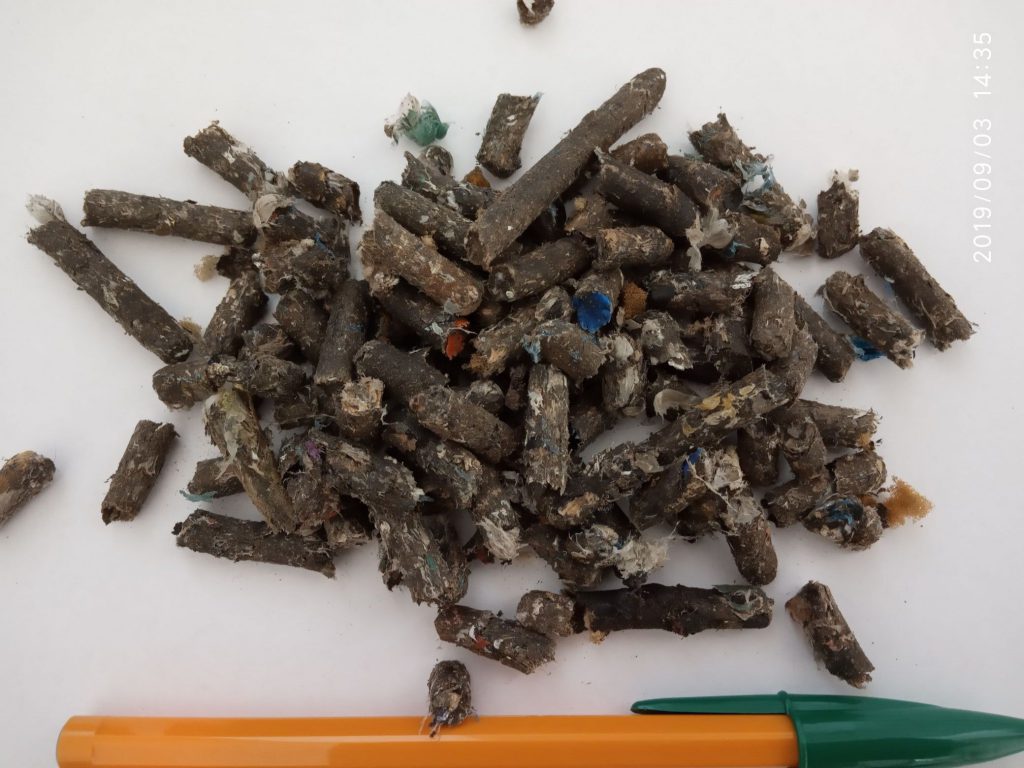

Pellets of RDF